The families of flowers and trees reproduce, seed reproduction (sexual reproduction); cuttings, grafting, layering, sub-beads (asexual reproduction); and recently many species of flowers and trees have been used for tissue culture, which is a new breeding method.
1. How to sow seed Seeds are obtained through a sexual process, and new individuals are bred with seeds. This new individual has both parental traits. The use of seeds to reproduce, the large amount of reproduction, the method is simple, the resulting seedlings root system integrity, robust growth, long life. Seeds are easy to carry, circulate, preserve and exchange. However, due to the large variability of seed propagation, it is often impossible to preserve its original good traits, so it is necessary to adopt some methods for the preservation of pure lines.
The sowing bed should be selected in the leeward sunny place of the garden. The soil is fertile, loose, and germinates at 16 to 20°C. Therefore, sowing is generally conducted in the spring and plum blossoms should be sown in the autumn. Drilling, on-demand, sowing depth, general large seed 0.4 cm, medium seed 0.2 cm, small seeds 0. l cm, spacing of O.2 cm. The seeds can be mixed evenly with 3 times the fine sand and then broadcasted. The seeds can also be broadcast in the fire basin. The thickness of the cover soil can be determined according to the size of the seeds. The depth of the cover of the small seeds is equivalent to 2 times the diameter of the seeds, and the large seeds can be used. Appropriately thickened, very fine seeds can be sieved and sieved immediately. After sowing, the board is used to press the surface of the soil and cover it with hay to keep the water and inhibit the growth of weeds until they are germinated and then removed. Usually use a fine hole watering can to sprinkle water, keep the soil dry, but should not be too wet, so as not to rot. When potting, the pots can be immersed in water to absorb moisture. Before the seeds are unearthed, the pots can be covered with a layer of glass or plastic film and newspapers, and the surface soil should be kept dry. After the seed leaves are unearthed, the lighter fertilizer and the seedlings are applied, and when the seeds grow to 4 to 5 true leaves, they are transplanted.
Before and after sowing, the soil should be kept moist and the water should be uniform. Always check the cover to prevent rain from flushing the bed. After the seed germinates, it is necessary to remove the covering immediately. Be sure to let the seedling gradually see the light. After a period of exercise, it can be completely exposed to the sun.
One-year-old flowers used to sow multiplication. Seeds suitable for spring sowing, such as cockscomb, morning glory, dill, a string of red, etc., are conducted from March to May. Autumn sowing, such as gold Chrysanthemum, Daisy, pansy, violet, snapdragon, etc., from late August to early October.
Drilling and sowing can be done. When the young seedlings are explanted, proper seedlings should be used. Don't hurt the root when transplanting, and pour enough water in time after transplanting.
In order to promote marigold, snapdragon, petunia, cosmos, red string, etc., plants increase branching and postpone flowering, and can be properly picked.
Daily management, we must pay attention to the removal of residual flowers, in order to facilitate the concentration of nutrients and extend the flowering period. Pay attention to watering in the morning and in the evening. In order to prevent the water temperature in summer from being too high, watering should not be done at noon, and watering should be performed during the warm days of noon in winter.
Apply enough basal fertilizer before sowing, such as compost, bone meal, alfalfa ash and cake fertilizer, and apply urea diluted liquid fertilizer as top dressing during the growth period. Should pay attention to loose soil and weeding on weekdays. Reduce water evaporation, increase soil temperature, promote nutrient decomposition.
In addition, we must pay attention to the germination ability of the seeds. The life span of different species is different depending on the type of flowers. For example, the seed vitality of delphinium, a bunch of red, pansy, lily, etc. is maintained for 1 to 2 years, while the seed viability of cyclamen, carnation and cockscomb is 4 to 5 years.
Aquatic flowers include lotus, water lily, and water hyacinth. They can be used both for sowing and breeding. Seeding and propagation of the skin to be worn, immersed in water to expand, into the shallow basin, the young leaves grow out of the water, and then moved into a large water tank or pool. The water depth is about 5 centimeters higher than that of the potted soil, and the germination can begin at 25 to 3O<0>C, and the water depth can be gradually increased after the seedlings have water.
2. How to insert cutting propagation is the most commonly used method of asexual reproduction in flower and tree propagation, with branch insertion (stem insertion), leaf insertion, and root insertion. The principle of cutting and planting is due to the regeneration of part of the plant body.
Cutting propagation can be propagated in spring, summer and autumn. If there is a courtyard small greenhouse, keep the temperature at 20 ~ 25 °C, can be breeding throughout the year.
The top soil of the plug bed can be made of bauxite, yellow sand, peat soil, perlite, and smelting slag, but it must be sterilized by high temperature to clean no bacteria. Insert a ditch or perforation on the insertion bed before inserting, then insert the cutting into 1/2 of the soil, compact the base, drench the water, usually pay attention to cover half of the shade, cover the plastic film to keep moist, but do not over-tide.
There are two kinds of cuttings, the first is the cuttings of the tender shoots, the new technology of the unliganded current year is about 10 cm with 2 leaflets, cuttings. However, it is better to keep the air humidity at 90%. Jasmine, gardenia, yucca, sticky sea bream, fuchsia, moon hung, rose, hibiscus, etc. can all be used for tenderness cuttings. The second is hardwood cuttings. The birch branches that have been lignined are cut to a length of 10 to 20 centimeters. They are smooth sloped and have 2 to 3 plump buds. In the cuttings of the year, there is a part of the old branch xylem (horse-shoe-shaped) that is easier to root; rafts, spring, forsythia, etc. are suitable for cutting in the autumn. In addition, leaf buds can also be inserted, that is, to take full shoots on the shoots, and bring one of the following leaves, 1/2 into the soil or basin soil, such as rubber trees, jasmine, oleander, hydrangea, Camellia and so are This method can be used.
Furthermore, root insertion can also be used. In winter, when trees sleep, their roots can be excavated, and cuttings with a length of 10 centimeters are cut, stored in wet sand, and inserted into soil in the second spring. This method can be used for Lamei, Lingxiao, Lagerstroemia, cherry blossom, peach, rose, clove, and wisteria.
In addition, there are water plugs, the cuttings will be placed on the floating objects, and the cuttings will be 1/2 left in the water. In a small container, the water must be changed frequently. In a large pool, it is not necessary to change the water. This method can be used for oleander, gardenia, ivy, variegated wood, rose, etc.
3. How to Graft Grafting is to use a part of the vegetative organ of plants to transfer to other plants. The branches used for grafting are called scions, and the buds used are called shoots. The grafted plants are called rootstocks, and the grafted seedlings are called grafted seedlings.
Grafting, generally in the spring or autumn plant growth when the grafting, the method of cutting, bud grafting, docking, splicing and so on.
1 Cut: Select and grow strong annual branches, cut about 10 cm, retain 2 to 3 buds, cut the lower part into a wedge shape of 1 to 2 cm, both sides must be smooth, one side is 30 mm long, and one side is 15 Millimeters, that is, the scion, cut the selected l-year-old robust rootstock branches, and then cut longitudinally in the middle or side of the cross-section. Open the rootstock branch and insert the scion into the mouth, but the two sides must form a layer. Align with each other, and then use a thin film to tie it. It can be fixed; it can also be covered with a plastic bag.
2 Buds: Buds with thick branches can be budded. Use side buds on full-grown and robust shoots, cut the leaves, leave the petioles, use a knife to cut a knife 2 to 3 mm above the leaf buds, and then cut it from the bottom of the leaf buds 5 to 6 mm upwards. The buds are cut into shields, and the xylem inside the shoots is removed and the "bud stalks" are prepared. A knife is cut across the dark side of the rootstock branch, and then a knife is cut to form a “D†mouth. The skin is picked up. The size is adapted to the “Bacteria scutellumâ€, and the budding scutellum is placed in the “D†mouth. The upper part is aligned with the "D" mouth and is finally fastened with a plastic film, but the buds and petioles should be exposed. After one week, the petioles fell off and the buds survived.
3 docking: Suitable for evergreen trees that are difficult to graft and survive. Move the scion and rootstock together, select the branches with similar thickness on the two plants, and cut off the 4-6 cm incisions in the opposite positions, the depth of which is 1/3-1/2, and then form the layers of the incisions to each other. After aligning and healing the incision, the scion is cut off from the lower part of the interface, and the buds on the rootstock are promptly removed after survival.
4 splicing: This method is used when the rootstock and scion's thickness differ greatly. The wedge-shaped cuttings are prepared first, and the spike-shaped noodles are required to be smooth, with similar size and length. Then the rootstock is truncated horizontally and the split is split longitudinally from the middle or side of the section. A scion can be inserted on each side of the crevice to make the lower wedge cuneate. The formation layer on the outside of the cut plane is aligned with the formation layer of the anvil crevice, and it can be tied with a plastic strip.
4. How to use the ramets to reproduce more for those mother plants whose roots must germinate and have strong tillering performance, or litchi, underground stem, and easy-to-root flowering shrubs. Generally, after the autumn, or in the early spring, the propagation of the seedlings is carried out, and the rooted tiller or the stem of the litchi is cut and planted.
Perennial flower, after the growth and development, the stems and leaves of the ground dead, underground roots dormant, and then re-birth and stems and leaves. In the dormant stage, the ramets are often used for reproduction The types of spring flowering should be divided into forests in autumn and winter. In summer, the cultivars should be bred in early spring. The method is to dig up the roots from the ground and divide the plant with buds. In the planting hole in the application of base fertilizer, covering the same depth with the original plant, in the spring before the germination of the root into the difficult to fat. The ramets, such as steppe and calla, can be used for propagation of the ramets.
Usually pay attention to weeding. Dead branches, stems, and leaves should be cut off during the winter season. For poor cold resistance, such as chrysanthemum, peony, orchid, Fu Lukao, Huang Kui, sesame, Ishigami, Campanulaceae, Spearmint, Ophiopogon japonicus, lily of the valley, mint, etc., can cover soil compost over the winter.
Generally, the ball flower can be mostly propagated by the ball. Most of them are spring planting, autumn season, and hibernation. The type of hibernation is usually planted in spring in April. In the summer, growth flourishes. After the fall, fertility ceases to occur, and winter sleeps. The ball is reportedly dug up and stored at the Wenyu area. Cold-tolerant species are generally planted in autumn. When it is cool, it grows and develops until it stops in the cold and continues to grow and blossom in the spring of the following year. In summer, flower bud differentiation occurs during dormancy. Lily, Shandan, tiger lily, daffodil, tulip, wind signal, when the dormant bulbs are stored, the ball should be dug out from the soil, and should not be exposed to the sun, and be placed in a cool, cool place; more than one bulbous root should be used for breeding; 4 years can reach the flowering standard. When planting, the ball should be shallow and dense; lily, hyacinth, large cone-shaped ball should be deep and sparse, Gladiolus and other flat ball depth declared appropriate.
5, how to pressure stripe layer propagation is actually a kind of cutting method that does not cut off the mother's body. It is mostly used for cutting flower that is not easy to survive. Deciduous trees are carried out from March to April, and evergreen trees are carried out during the rainy season. The method is to overwhelm the branches close to the ground and bury it in a trench of 8 to 10 cm in depth. The top of the branches is exposed on the ground and then fixed with a wooden hook. After the shoots have been rooted and the seedlings have grown, they are cut off from the mother plant to form an independent new plant for planting.
In addition, if the branches are strong and the branches do not bend easily, the lower part of the branches may be wounded or peeled with a knife, and the soil may be cultivated in the lower part of the branches so that a new report may be issued by the upper minister and the buds will germinate until the spring of the next year is cut from the lower part of the new root. Can be divided into branches.
For those branches that are hard and difficult to bend. The high pressure can be performed, ie, the biennial branches selected on the mother plant are subjected to ring peeling of l-1.5 cm long, and the relative bamboo tube or plastic film is used to hold the skin at the peeling place, which is filled with moss, straw ash and culture. , And keep it moist, until the upper part of the incision is cut off the mother beads, to form a new strain.
The bulbous flowers are more tolerant to drought, and the looser humus soil should be properly watered except when the fertility period is dry. The ball newspaper must be stored before entering the dormant period. The balls can cover the winter, harvested every other year; cannas, dahlias, lilies to keep moist, do not make the ball very much lose moisture, into the fine sand, glutinous rice, fine sawdust. Gladiolus requires drying, putting it into a dry and well-ventilated room, especially when it is stored in the summer, it should be kept dry and cool, otherwise it is easy to be damp and rotten.
Melting point 3 °C(lit.)
Boiling point 258 °C(lit.)
density 1.375 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
refractive index n20/D 1.559(lit.)
storage temp. 2-8°C
solubility Miscible with benzene, chloroform, dimethyl sulfoxide and carbon tetrachloride.
form Liquid
color Clear yellow to brown
Specific Gravity 1.394 (25℃)
Water Solubility reacts
1. How to sow seed Seeds are obtained through a sexual process, and new individuals are bred with seeds. This new individual has both parental traits. The use of seeds to reproduce, the large amount of reproduction, the method is simple, the resulting seedlings root system integrity, robust growth, long life. Seeds are easy to carry, circulate, preserve and exchange. However, due to the large variability of seed propagation, it is often impossible to preserve its original good traits, so it is necessary to adopt some methods for the preservation of pure lines.
The sowing bed should be selected in the leeward sunny place of the garden. The soil is fertile, loose, and germinates at 16 to 20°C. Therefore, sowing is generally conducted in the spring and plum blossoms should be sown in the autumn. Drilling, on-demand, sowing depth, general large seed 0.4 cm, medium seed 0.2 cm, small seeds 0. l cm, spacing of O.2 cm. The seeds can be mixed evenly with 3 times the fine sand and then broadcasted. The seeds can also be broadcast in the fire basin. The thickness of the cover soil can be determined according to the size of the seeds. The depth of the cover of the small seeds is equivalent to 2 times the diameter of the seeds, and the large seeds can be used. Appropriately thickened, very fine seeds can be sieved and sieved immediately. After sowing, the board is used to press the surface of the soil and cover it with hay to keep the water and inhibit the growth of weeds until they are germinated and then removed. Usually use a fine hole watering can to sprinkle water, keep the soil dry, but should not be too wet, so as not to rot. When potting, the pots can be immersed in water to absorb moisture. Before the seeds are unearthed, the pots can be covered with a layer of glass or plastic film and newspapers, and the surface soil should be kept dry. After the seed leaves are unearthed, the lighter fertilizer and the seedlings are applied, and when the seeds grow to 4 to 5 true leaves, they are transplanted.
Before and after sowing, the soil should be kept moist and the water should be uniform. Always check the cover to prevent rain from flushing the bed. After the seed germinates, it is necessary to remove the covering immediately. Be sure to let the seedling gradually see the light. After a period of exercise, it can be completely exposed to the sun.
One-year-old flowers used to sow multiplication. Seeds suitable for spring sowing, such as cockscomb, morning glory, dill, a string of red, etc., are conducted from March to May. Autumn sowing, such as gold Chrysanthemum, Daisy, pansy, violet, snapdragon, etc., from late August to early October.
Drilling and sowing can be done. When the young seedlings are explanted, proper seedlings should be used. Don't hurt the root when transplanting, and pour enough water in time after transplanting.
In order to promote marigold, snapdragon, petunia, cosmos, red string, etc., plants increase branching and postpone flowering, and can be properly picked.
Daily management, we must pay attention to the removal of residual flowers, in order to facilitate the concentration of nutrients and extend the flowering period. Pay attention to watering in the morning and in the evening. In order to prevent the water temperature in summer from being too high, watering should not be done at noon, and watering should be performed during the warm days of noon in winter.
Apply enough basal fertilizer before sowing, such as compost, bone meal, alfalfa ash and cake fertilizer, and apply urea diluted liquid fertilizer as top dressing during the growth period. Should pay attention to loose soil and weeding on weekdays. Reduce water evaporation, increase soil temperature, promote nutrient decomposition.
In addition, we must pay attention to the germination ability of the seeds. The life span of different species is different depending on the type of flowers. For example, the seed vitality of delphinium, a bunch of red, pansy, lily, etc. is maintained for 1 to 2 years, while the seed viability of cyclamen, carnation and cockscomb is 4 to 5 years.
Aquatic flowers include lotus, water lily, and water hyacinth. They can be used both for sowing and breeding. Seeding and propagation of the skin to be worn, immersed in water to expand, into the shallow basin, the young leaves grow out of the water, and then moved into a large water tank or pool. The water depth is about 5 centimeters higher than that of the potted soil, and the germination can begin at 25 to 3O<0>C, and the water depth can be gradually increased after the seedlings have water.
2. How to insert cutting propagation is the most commonly used method of asexual reproduction in flower and tree propagation, with branch insertion (stem insertion), leaf insertion, and root insertion. The principle of cutting and planting is due to the regeneration of part of the plant body.
Cutting propagation can be propagated in spring, summer and autumn. If there is a courtyard small greenhouse, keep the temperature at 20 ~ 25 °C, can be breeding throughout the year.
The top soil of the plug bed can be made of bauxite, yellow sand, peat soil, perlite, and smelting slag, but it must be sterilized by high temperature to clean no bacteria. Insert a ditch or perforation on the insertion bed before inserting, then insert the cutting into 1/2 of the soil, compact the base, drench the water, usually pay attention to cover half of the shade, cover the plastic film to keep moist, but do not over-tide.
There are two kinds of cuttings, the first is the cuttings of the tender shoots, the new technology of the unliganded current year is about 10 cm with 2 leaflets, cuttings. However, it is better to keep the air humidity at 90%. Jasmine, gardenia, yucca, sticky sea bream, fuchsia, moon hung, rose, hibiscus, etc. can all be used for tenderness cuttings. The second is hardwood cuttings. The birch branches that have been lignined are cut to a length of 10 to 20 centimeters. They are smooth sloped and have 2 to 3 plump buds. In the cuttings of the year, there is a part of the old branch xylem (horse-shoe-shaped) that is easier to root; rafts, spring, forsythia, etc. are suitable for cutting in the autumn. In addition, leaf buds can also be inserted, that is, to take full shoots on the shoots, and bring one of the following leaves, 1/2 into the soil or basin soil, such as rubber trees, jasmine, oleander, hydrangea, Camellia and so are This method can be used.
Furthermore, root insertion can also be used. In winter, when trees sleep, their roots can be excavated, and cuttings with a length of 10 centimeters are cut, stored in wet sand, and inserted into soil in the second spring. This method can be used for Lamei, Lingxiao, Lagerstroemia, cherry blossom, peach, rose, clove, and wisteria.
In addition, there are water plugs, the cuttings will be placed on the floating objects, and the cuttings will be 1/2 left in the water. In a small container, the water must be changed frequently. In a large pool, it is not necessary to change the water. This method can be used for oleander, gardenia, ivy, variegated wood, rose, etc.
3. How to Graft Grafting is to use a part of the vegetative organ of plants to transfer to other plants. The branches used for grafting are called scions, and the buds used are called shoots. The grafted plants are called rootstocks, and the grafted seedlings are called grafted seedlings.
Grafting, generally in the spring or autumn plant growth when the grafting, the method of cutting, bud grafting, docking, splicing and so on.
1 Cut: Select and grow strong annual branches, cut about 10 cm, retain 2 to 3 buds, cut the lower part into a wedge shape of 1 to 2 cm, both sides must be smooth, one side is 30 mm long, and one side is 15 Millimeters, that is, the scion, cut the selected l-year-old robust rootstock branches, and then cut longitudinally in the middle or side of the cross-section. Open the rootstock branch and insert the scion into the mouth, but the two sides must form a layer. Align with each other, and then use a thin film to tie it. It can be fixed; it can also be covered with a plastic bag.
2 Buds: Buds with thick branches can be budded. Use side buds on full-grown and robust shoots, cut the leaves, leave the petioles, use a knife to cut a knife 2 to 3 mm above the leaf buds, and then cut it from the bottom of the leaf buds 5 to 6 mm upwards. The buds are cut into shields, and the xylem inside the shoots is removed and the "bud stalks" are prepared. A knife is cut across the dark side of the rootstock branch, and then a knife is cut to form a “D†mouth. The skin is picked up. The size is adapted to the “Bacteria scutellumâ€, and the budding scutellum is placed in the “D†mouth. The upper part is aligned with the "D" mouth and is finally fastened with a plastic film, but the buds and petioles should be exposed. After one week, the petioles fell off and the buds survived.
3 docking: Suitable for evergreen trees that are difficult to graft and survive. Move the scion and rootstock together, select the branches with similar thickness on the two plants, and cut off the 4-6 cm incisions in the opposite positions, the depth of which is 1/3-1/2, and then form the layers of the incisions to each other. After aligning and healing the incision, the scion is cut off from the lower part of the interface, and the buds on the rootstock are promptly removed after survival.
4 splicing: This method is used when the rootstock and scion's thickness differ greatly. The wedge-shaped cuttings are prepared first, and the spike-shaped noodles are required to be smooth, with similar size and length. Then the rootstock is truncated horizontally and the split is split longitudinally from the middle or side of the section. A scion can be inserted on each side of the crevice to make the lower wedge cuneate. The formation layer on the outside of the cut plane is aligned with the formation layer of the anvil crevice, and it can be tied with a plastic strip.
4. How to use the ramets to reproduce more for those mother plants whose roots must germinate and have strong tillering performance, or litchi, underground stem, and easy-to-root flowering shrubs. Generally, after the autumn, or in the early spring, the propagation of the seedlings is carried out, and the rooted tiller or the stem of the litchi is cut and planted.
Perennial flower, after the growth and development, the stems and leaves of the ground dead, underground roots dormant, and then re-birth and stems and leaves. In the dormant stage, the ramets are often used for reproduction The types of spring flowering should be divided into forests in autumn and winter. In summer, the cultivars should be bred in early spring. The method is to dig up the roots from the ground and divide the plant with buds. In the planting hole in the application of base fertilizer, covering the same depth with the original plant, in the spring before the germination of the root into the difficult to fat. The ramets, such as steppe and calla, can be used for propagation of the ramets.
Usually pay attention to weeding. Dead branches, stems, and leaves should be cut off during the winter season. For poor cold resistance, such as chrysanthemum, peony, orchid, Fu Lukao, Huang Kui, sesame, Ishigami, Campanulaceae, Spearmint, Ophiopogon japonicus, lily of the valley, mint, etc., can cover soil compost over the winter.
Generally, the ball flower can be mostly propagated by the ball. Most of them are spring planting, autumn season, and hibernation. The type of hibernation is usually planted in spring in April. In the summer, growth flourishes. After the fall, fertility ceases to occur, and winter sleeps. The ball is reportedly dug up and stored at the Wenyu area. Cold-tolerant species are generally planted in autumn. When it is cool, it grows and develops until it stops in the cold and continues to grow and blossom in the spring of the following year. In summer, flower bud differentiation occurs during dormancy. Lily, Shandan, tiger lily, daffodil, tulip, wind signal, when the dormant bulbs are stored, the ball should be dug out from the soil, and should not be exposed to the sun, and be placed in a cool, cool place; more than one bulbous root should be used for breeding; 4 years can reach the flowering standard. When planting, the ball should be shallow and dense; lily, hyacinth, large cone-shaped ball should be deep and sparse, Gladiolus and other flat ball depth declared appropriate.
5, how to pressure stripe layer propagation is actually a kind of cutting method that does not cut off the mother's body. It is mostly used for cutting flower that is not easy to survive. Deciduous trees are carried out from March to April, and evergreen trees are carried out during the rainy season. The method is to overwhelm the branches close to the ground and bury it in a trench of 8 to 10 cm in depth. The top of the branches is exposed on the ground and then fixed with a wooden hook. After the shoots have been rooted and the seedlings have grown, they are cut off from the mother plant to form an independent new plant for planting.
In addition, if the branches are strong and the branches do not bend easily, the lower part of the branches may be wounded or peeled with a knife, and the soil may be cultivated in the lower part of the branches so that a new report may be issued by the upper minister and the buds will germinate until the spring of the next year is cut from the lower part of the new root. Can be divided into branches.
For those branches that are hard and difficult to bend. The high pressure can be performed, ie, the biennial branches selected on the mother plant are subjected to ring peeling of l-1.5 cm long, and the relative bamboo tube or plastic film is used to hold the skin at the peeling place, which is filled with moss, straw ash and culture. , And keep it moist, until the upper part of the incision is cut off the mother beads, to form a new strain.
The bulbous flowers are more tolerant to drought, and the looser humus soil should be properly watered except when the fertility period is dry. The ball newspaper must be stored before entering the dormant period. The balls can cover the winter, harvested every other year; cannas, dahlias, lilies to keep moist, do not make the ball very much lose moisture, into the fine sand, glutinous rice, fine sawdust. Gladiolus requires drying, putting it into a dry and well-ventilated room, especially when it is stored in the summer, it should be kept dry and cool, otherwise it is easy to be damp and rotten.
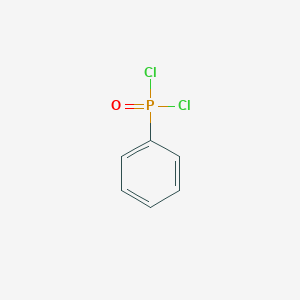
Phenylphosphonic Dichloride Basic Information
Product Name: Phenylphosphonic dichloride
CAS: 824-72-6
MF: C6H5Cl2OP
MW: 194.98
EINECS: 212-534-3
Mol File: 824-72-6.mol
Phenylphosphonic Dichloride Structure
Melting point 3 °C(lit.)
Boiling point 258 °C(lit.)
density 1.375 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
refractive index n20/D 1.559(lit.)
storage temp. 2-8°C
solubility Miscible with benzene, chloroform, dimethyl sulfoxide and carbon tetrachloride.
form Liquid
color Clear yellow to brown
Specific Gravity 1.394 (25℃)
Water Solubility reacts
Phenylphosphonic Dichloride CAS No.824-72-6
phenylphosphonic dichloride,phenylphosphonic dichloride wiki,phenylphosphonic dichloride msds,phenylphosphonic dichloride reaction,phenylphosphonic acid dichloride
ShanDong YingLang Chemical Co.,LTD , https://www.sdylhgtrade.com